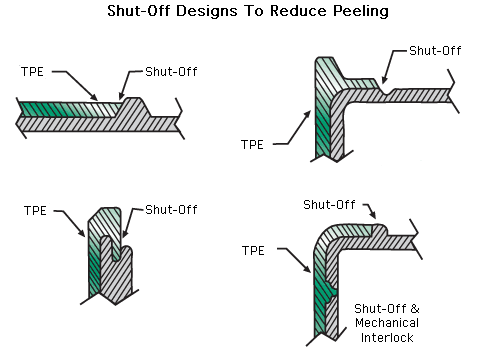
Shutoffs in injection molding refer to areas within a mold where two mold components come together to create a seal, preventing the flow of molten plastic beyond a certain point. These shutoffs are crucial for defining the boundaries of different parts of the mold, controlling the flow of plastic, and ensuring the precise formation of the molded part. Proper shutoff design is essential for maintaining part integrity and avoiding defects.
Functions of Shutoffs
- Control of Material Flow:
- Shutoffs help control where the plastic flows within the mold, ensuring that it only fills the desired cavities and features.
- Formation of Part Features:
- By creating precise seals, shutoffs help form specific part features such as holes, slots, and complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to mold otherwise.
- Prevention of Flash:
- Proper shutoff design prevents flash, which is excess material that escapes from the cavity and forms thin, unwanted layers on the part surface.
- Separation of Mold Sections:
- Shutoffs enable the separation of different mold sections, such as moving and stationary parts, ensuring they come together accurately during the molding process.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Types of Shutoffs
- Metal-to-Metal Shutoffs:
- These shutoffs rely on the precise contact between two metal surfaces within the mold.
- Applications: Used for high-precision parts where minimal tolerance and tight seals are required.
- Advantages: Provides a very accurate shutoff, preventing any leakage of molten plastic.
- Parting Line Shutoffs:
- Located along the parting line where the two halves of the mold meet.
- Applications: Common in molds with simple geometries and where the parting line can be placed strategically.
- Advantages: Easy to machine and maintain, but may require careful design to avoid visible parting lines on the finished part.
- Side Shutoffs:
- Used for features that are perpendicular to the mold opening direction.
- Applications: Ideal for creating side holes, slots, or other features that require a side action.
- Advantages: Allows for more complex part geometries without compromising the mold’s functionality.
- Interlocking Shutoffs:
- Designed to interlock and create a more secure shutoff.
- Applications: Used in situations where the plastic might tend to flow through tight spaces or around corners.
- Advantages: Provides a more robust seal, reducing the risk of flash and ensuring precise part formation.
Design Considerations for Shutoffs
- Accuracy and Precision:
- Shutoff surfaces must be machined with high precision to ensure a perfect seal. Any gaps or misalignment can lead to defects such as flash or incomplete fills.
- Material Selection:
- The material used for the mold, typically steel or aluminum, must be durable and capable of maintaining the shutoff integrity over many cycles.
- Maintenance and Wear:
- Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure that shutoff surfaces remain clean and free of wear. Worn shutoffs can lead to leakage and part defects.
- Thermal Expansion:
- The mold design must account for thermal expansion and contraction to maintain tight shutoffs throughout the molding process. Differential expansion between mold components can affect shutoff integrity.
- Complexity of Part Geometry:
- The complexity of the part being molded will influence the type and design of shutoffs required. More complex geometries may require multiple or specialized shutoffs.
Common Applications of Shutoffs
- Automotive Components:
- Used in molding complex parts such as dashboards, door panels, and engine components that require precise feature definition.
- Consumer Electronics:
- Essential for creating detailed and precise housings and internal structures in devices such as smartphones, laptops, and cameras.
- Medical Devices:
- Critical for molding parts with intricate features and high precision, such as connectors, housings, and intricate components.
- Industrial Equipment:
- Used in producing robust and precise components for machinery, tools, and industrial devices.

As a leading mold injection manufacturer in China, we deliver superior molds for various industries. Our state-of-the-art facilities and expert team ensure top-notch quality and timely delivery. Contact us now for a competitive quote!
Conclusion
Shutoffs are vital in injection molding for controlling material flow, forming precise part features, and preventing defects. Proper design and maintenance of shutoffs are essential for ensuring high-quality molded parts. By understanding the different types of shutoffs and their applications, mold designers can optimize their molds to achieve better performance, accuracy, and reliability in the injection molding process.
Related Conten: https://www.m-dtg.com/service/plastic-blow-molding/