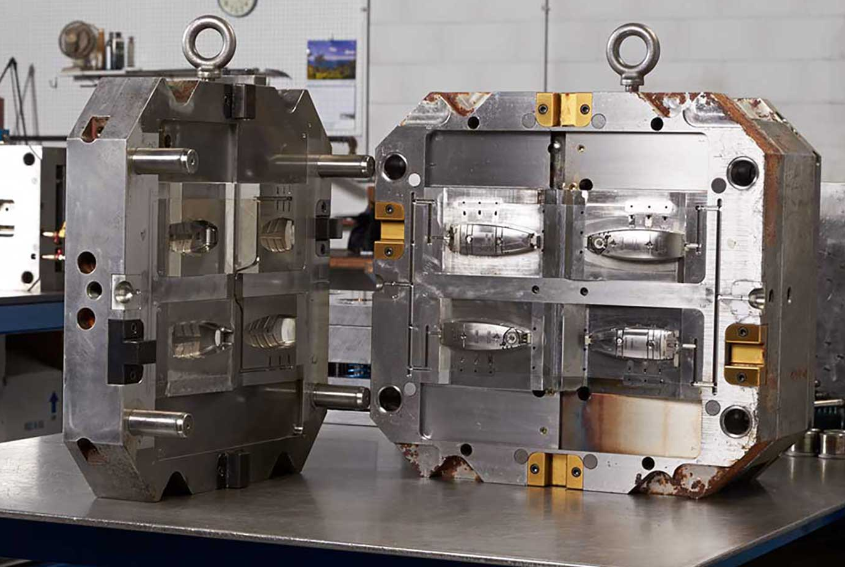
The lifespan of injection molds depends on various factors, including the mold material, design, maintenance, and the type of plastic being molded. Here’s a detailed overview of the key factors influencing the longevity of injection molds:
Factors Affecting Injection Mold Lifespan
- Mold Material:
- Hardened Steel Molds: Typically last the longest, often exceeding 1 million cycles. Suitable for high-volume production.
- Pre-Hardened Steel Molds: Usually last between 500,000 to 1 million cycles. Suitable for moderate to high-volume production.
- Aluminum Molds: Generally have a shorter lifespan, ranging from 10,000 to 100,000 cycles. Ideal for prototyping and low to medium-volume production.
- Beryllium-Copper Alloy Molds: Known for excellent thermal conductivity and typically last between 100,000 to 1 million cycles, depending on the application.
- Design and Manufacturing Quality:
- Precision and Accuracy: High-quality design and precision manufacturing can extend the mold’s lifespan by reducing wear and tear.
- Cooling System: Effective cooling systems prevent overheating, reducing thermal stress and prolonging mold life.
- Surface Treatment: Treatments like nitriding or hardening can enhance mold durability and resistance to wear.
- Maintenance and Care:
- Regular Cleaning: Frequent cleaning prevents buildup of residues and contaminants that can cause wear.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of moving parts reduces friction and wear.
- Inspection and Repairs: Regular inspection and timely repairs prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems.
- Type of Plastic Material:
- Abrasive Materials: Plastics with fillers or reinforcements (e.g., glass fibers) can cause more wear on the mold, reducing its lifespan.
- Non-Abrasive Materials: Pure polymers or non-abrasive plastics cause less wear, extending mold life.
- Production Volume and Cycle Times:
- High-Volume Production: Molds used in continuous high-volume production environments typically experience more wear and require more frequent maintenance.
- Cycle Times: Shorter cycle times can increase thermal and mechanical stress on the mold, potentially reducing its lifespan.
Typical Lifespans of Injection Molds
- Prototyping Molds:
- Usually made from softer materials like aluminum.
- Lifespan ranges from 10,000 to 100,000 cycles.
- Production Molds:
- Made from pre-hardened or hardened steel.
- Lifespan typically ranges from 500,000 to over 1 million cycles.
- High-Precision Molds:
- Used for producing high-precision parts with stringent quality requirements.
- Lifespan can exceed 1 million cycles with proper maintenance.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Extending the Lifespan of Injection Molds
- Proper Design:
- Design the mold with uniform wall thickness and appropriate draft angles to reduce stress and wear.
- Include features like venting channels and adequate cooling to enhance mold performance.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Implement a preventive maintenance schedule that includes regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection.
- Address wear and damage promptly to prevent further deterioration.
- Use of Mold Coatings:
- Apply coatings such as PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) or nitriding to enhance surface hardness and wear resistance.
- Optimized Processing Conditions:
- Optimize injection molding parameters (temperature, pressure, cooling time) to minimize stress on the mold.
- Use appropriate cycle times to balance production efficiency and mold longevity.
Conclusion
The lifespan of injection molds varies widely based on material, design, maintenance, and usage factors. By selecting the appropriate mold material, ensuring high-quality design and manufacturing, and adhering to regular maintenance practices, manufacturers can maximize the lifespan of their injection molds, ensuring consistent production quality and cost-effectiveness.
Related Conten: Custom Molders Corp