Transfer molding is a manufacturing procedure that integrates the functions of both injection molding and compression molding. It involves using a pre-measured quantity of raw material. It is warmed and filled into a chamber known as the pot situated on top of the mold and mildew. The product consisted of in the pot, which is generally a warmed tank, is utilized for a solitary cycle and can be utilized to fill up numerous mold and mildew cavities all at once. A piston is then employed to drive the polymer right into a preheated mold and mildew through a network referred to as a sprue. The mold and mildew stays in a shut placement till the product included within has completely cured.
The mold and mildew utilized in the transfer molding procedure is a hollow area, or cavity, which has a within surface that specifies the form of the wanted component. This technique supplies several benefits over other molding strategies, such as compression molding. These benefits include: shorter production cycle times, greater dental caries matter, and better style versatility. In this short article, we will delve deeper into how transfer molding functions, discover its advantages for various industries, and more.
What Is Transfer Molding?
Transfer molding is a production process that requires pressing a casting product right into a closed mold and mildew. Transfer molding stands out from compression molding because it utilizes a confined mold and mildew. It includes transferring a gauged amount of product, in a preheated and softened state, into a shut mold and mildew cavity under pressure. The product is after that healed or solidified to create the wanted shape.
Transfer molding is mostly made use of to enclose digital parts in rubber or plastic. It enables the fabrication of plastic parts with steel inserts, such as prongs or semiconductor chips. Pins, studs, connectors, and molded terminals can all be created utilizing this approach. Moreover, transfer molding permits the manufacturing of parts with sharper edges and edges. This function is specifically helpful in industries such as hydraulics, where the sealing of liquids is vital. Lip seals, which are utilized to prevent liquid leakage in hydraulic systems, usually require specific edges to ensure reliable securing. Transfer molding allows the development of sharp and well-defined edges, which improves the efficiency and integrity of such seals.
The Transfer Molding Refine
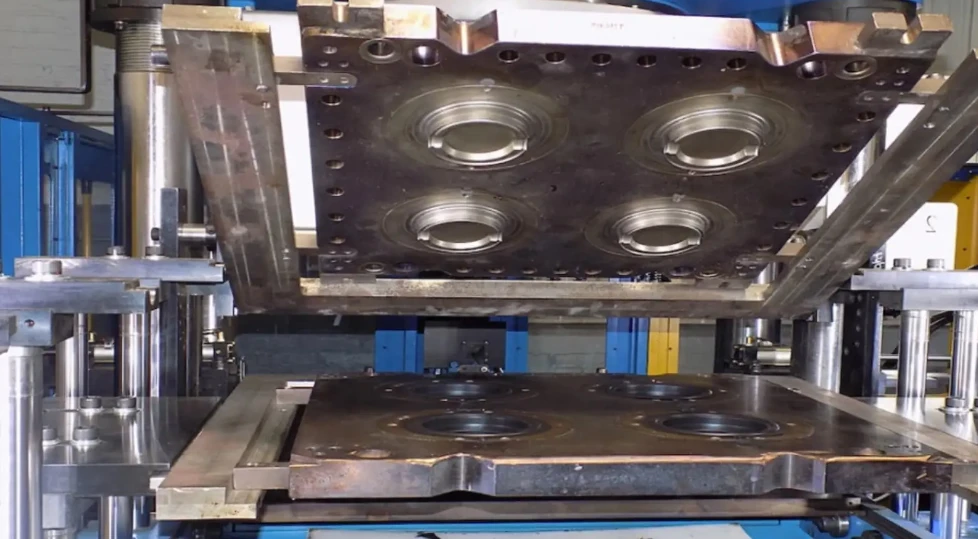
Transfer molding is a procedure that incorporates compression and transfer of the polymer cost. It involves moving a pre-weighed polymer charge to a mold dental caries from a heated transfer pot. The fee is fed into the transfer pot by gravity feed, yet it is not straight infused into the mold tooth cavity. Rather, it is presented into the mold tooth cavity under the pressure of a bettor. The shaped part is after that ejected utilizing an ejector pin after the resin has actually had time to heal. Normal post-processing demands include trimming off the sprue and entrance. Number 1 below illustrates the fundamental procedure of transfer molding:
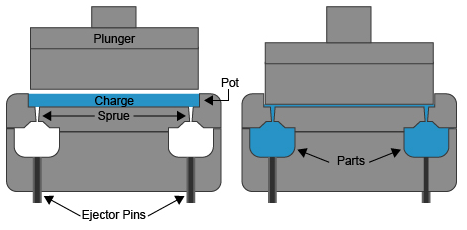
The period of the transfer molding process can differ depending upon a number of variables, including the size and complexity of the part, the type of product being used, and the details manufacturing demands. Contrasted to compression molding, transfer molding usually provides quicker cycle times because of its capacity to inject the product into the mold under higher pressure. On the other hand, shot molding commonly has shorter cycle times than transfer molding, as it involves injecting molten product straight right into the mold and mildew at high speed.
RTM (Material Transfer Molding) is a procedure where fluid material is infused into a shut mold having pre-placed reinforcements and afterwards healed to develop a solid composite component. HP-RTM (High-Pressure Resin Transfer Molding) is a variant of RTM that utilizes greater injection pressures to reduce material injection times and enhance component combination. However, when it comes to high-pressure material transfer molding (HP-RTM), the resin injection time is usually around 1-5 minutes. This is considerably shorter than typical material transfer molding (RTM), which can take approximately 30-60 mins. This much shorter manufacturing cycle time makes HP-RTM an appealing production process for huge composite parts in the automobile industry.
Transfer Molding Vs. Injection Molding: Similarities and Differences
Transfer molding and shot molding are both prominent strategies for producing plastic components, yet they vary in several methods. In transfer molding, the material is generally fed right into a heated chamber through a screw, and then a bettor compels it right into a mold cavity. Injection molding, on the other hand, makes use of a reciprocating screw to melt and infuse the material directly into the mold tooth cavity. Transfer molding is typically used for coverings and low-volume manufacturing of less complex molds, while shot molding is well-suited for bigger, thin-walled parts. Shot molding provides greater manufacturing rates and better precision, while transfer molding provides reduced tooling complexity. Transfer molding requires preparing the raw material before it is pushed into the mold, boosting handling time and elevating prices. In contrast, shot molding instantly mixes and readies the product, permitting instant manufacturing. This difference in material prep work results in varying manufacturing timelines and expense frameworks. Making the choice in between transfer molding and shot molding depends on details requirements and constraints. For additional information, see our guide on Infused Plastics.
Materials Used in Transfer Molding
A few of the materials used in transfer molding include:
Epoxy
Epoxy is a flexible thermosetting polymer that displays exceptional electrical insulation residential properties and high chemical resistance. Its reduced viscosity allows for easy circulation throughout the transfer molding procedure, ensuring precise duplication of mold information. Epoxy can be breakable and may need post-curing procedures for optimum mechanical toughness.
Silicone
Silicone is a versatile polymer renowned for its flexibility, sturdiness, temperature resistance, and biocompatibility, making it extremely preferable for different applications. However, contrasted to various other materials, silicone can be fairly much more pricey because of its unique homes and manufacturing procedures. Furthermore, the curing time of silicone can be longer compared to products such as epoxy material. For more details, see our overview on What is Silicone.
Polymers
Polymers like polyurethane and polyester appropriate for transfer molding because of their desirable residential properties. Polyurethane provides outstanding toughness, chemical resistance, and versatility, making it suitable for applications needing longevity and flexibility. Polyester, on the other hand, offers excellent warmth resistance and mechanical toughness. These features allow both polyurethane and polyester to withstand the warm and pressure associated with transfer molding processes. To find out more, see our overview on Polymer Residence.
Rubber
Rubber describes elastomers with high elasticity and durability. Rubber materials, whether natural rubber or synthetic elastomers, can be quickly processed making use of transfer molding. Depending on the type of rubber, post-curing or vulcanization procedures may be needed to accomplish ideal buildings. To learn more, see our overview on TPR Product.
Plastics
Plastics like polypropylene and polycarbonate appropriate for transfer molding as a result of their beneficial attributes. Polypropylene exhibits excellent flow homes, enabling it to fill up intricate mold dental caries easily. It likewise uses good chemical resistance and dimensional stability. Polycarbonate, on the other hand, has high impact stamina, transparency, and heat resistance, making it excellent for applications calling for these residential properties. Some plastic materials might have constraints in terms of temperature resistance, dimensional security, or strength, needing careful selection for certain applications.
Products made by transfer molding are renowned for their outstanding sturdiness. Since they have a great strength-to-weight proportion, they can be made use of for various points, consisting of heavy items. The enhancement of strengthening fibers and the high strength-to-weight proportion that is enabled with a fiber lots of 25– 50% additionally contribute to move molding’s enhanced high quality and resilience, particularly in thicker-walled components.
Transfer-molded items can be warmth resistant, depending on the specific product utilized in the process. Particular materials, such as silicone and particular thermosetting plastics, exhibit excellent warm resistance. They can hold up against high temperatures without contortion or destruction. It is very important to remember that not all thermoplastics are suitable for transfer molding, although specific materials can offer warm resistance when utilized in this process. Polyethylene is one kind of polycarbonate that has a credibility for being much less suitable for transfer molding as a result of its weak heat resistance. Due to its low melting point, polyethylene might not have the ability to stand up to the high temperatures and pressures used in transfer molding. To make sure the wanted warmth resistance for a specific application, it is encouraged to consult the product specs and execute the needed testing.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Usual Applications of Transfer Molded Products
Transfer molding locates applications in different industries:
- Electric Sector: Adapter seals can be molded around cords, with ignition system wires being a common instance.
- Gas Sector: Transfer molding is made use of to create metal-to-rubber face seals, supplying a trusted user interface for gas valves.
- Clinical Sector: In the medical area, transfer molding is extensively utilized for silicone overmolding, specifically for clinical tool deals with and surgical tool components.
The Pros of Transfer Molding
Advantages include:
- Permits the easy assimilation of inserts, such as steel elements of electronic components, into the molded item
- Enables detailed styles with sharper edges, giving better layout adaptability contrasted to various other molding techniques
- Creates get rid of very little or no flash, eliminating the requirement for added deflashing procedures
Usually includes simpler pot and plunger styles, causing reduced tooling and equipment expenses compared to various other molding methods
The Disadvantages of Transfer Molding
Drawbacks include:
Has the capacity for product wastage, specifically throughout the preparation and transfer phases. This is mainly as a result of using sprue and overflow grooves, which can lead to excess product that is disposed of. Furthermore, transfer molding is not for reusing thermosetting polymers into the process, additional raising manufacturing prices and ecological influence.
Typically has a slower production rate contrasted to injection molding as a result of the extra steps associated with material preparation and transfer
Air can get caught in the mold and mildew throughout the transfer procedure. This can result in problems in the end product and require additional measures to guarantee air is correctly evacuatedSummary.