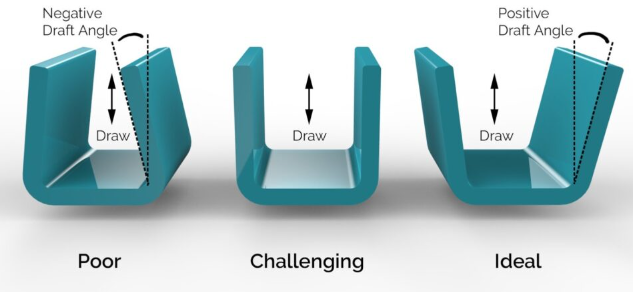
A draft angle in injection molding refers to a slight taper applied to the vertical walls of a molded part to facilitate its removal from the mold. Incorporating draft angles is essential in the design of injection-molded parts to ensure smooth ejection, minimize defects, and extend the mold’s lifespan.
Importance of Draft Angles
- Easier Ejection:
- Draft angles reduce the friction between the molded part and the mold walls, allowing the part to be ejected smoothly without sticking.
- Preventing Damage:
- Proper draft angles help avoid damage to the part and mold during ejection, reducing the likelihood of scratches, drag marks, or deformation.
- Improving Mold Longevity:
- By facilitating easier ejection, draft angles reduce the wear and tear on the mold, extending its operational life.
- Enhancing Part Quality:
- Draft angles help maintain the integrity and quality of the molded part, ensuring consistent and accurate dimensions.
Typical Draft Angle Recommendations
- The recommended draft angle depends on various factors such as the material used, the part’s geometry, and the mold surface finish. Generally, a draft angle of 1-2 degrees per side is considered adequate for most materials and part designs. However, more complex parts or those with deeper cavities might require larger draft angles, sometimes up to 5 degrees or more.
Factors Influencing Draft Angle
- Material:
- Different materials have different shrinkage and friction characteristics. For example, materials with higher shrinkage rates may require larger draft angles.
- Part Geometry:
- Parts with deeper or more complex cavities usually need larger draft angles to ensure smooth ejection.
- Surface Finish:
- A rough mold surface increases friction, necessitating a larger draft angle, while a polished surface allows for smaller draft angles.
- Ejection Method:
- The method and force used for ejection also influence the required draft angle. Ejection pins, air blasts, or stripper plates can affect the ease of part removal.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Designing with Draft Angles
When designing an injection-molded part, it’s crucial to incorporate draft angles into all vertical faces. Here are some guidelines:
- Exterior Faces:
- Apply the draft angle outward from the mold cavity to ensure the part can be ejected without interference.
- Interior Faces:
- Apply the draft angle inward toward the core of the mold to facilitate ejection of internal features.
- Ribs and Bosses:
- Ensure that features like ribs and bosses also have appropriate draft angles to prevent sticking and damage.
Example:
Imagine a plastic cup being produced through injection molding. If the walls of the cup are perfectly vertical (0-degree draft), it will be challenging to eject the cup from the mold without causing damage. By applying a slight taper (draft angle) to the walls, the cup can be ejected smoothly and without defects.
Conclusion
Draft angles are a critical aspect of injection mold design, ensuring parts are ejected smoothly and without damage. By reducing friction and wear on the mold, draft angles help maintain part quality and extend the mold’s lifespan. Properly designed draft angles enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the injection molding process, leading to better overall production outcomes.
Related Conten: Plastic Injection Molding