Injection molds are essential tools in mass manufacturing, enabling the production of consistent and high-quality plastic parts. The process of making injection molds involves several stages, from design to final production. Here’s an in-depth look at how injection molds are made for mass manufacturing:
1. Design Phase
A. Concept and Requirements
- Product Design: The process begins with the design of the product to be manufactured. Detailed CAD (Computer-Aided Design) models are created, specifying all dimensions, features, and tolerances.
- Material Selection: The type of plastic material to be used influences the mold design, considering factors like shrinkage, melting temperature, and flow characteristics.
- Mold Specifications: Determine the number of cavities (single or multi-cavity mold), mold base material (typically hardened steel or aluminum), and mold life expectancy.
B. Mold Design
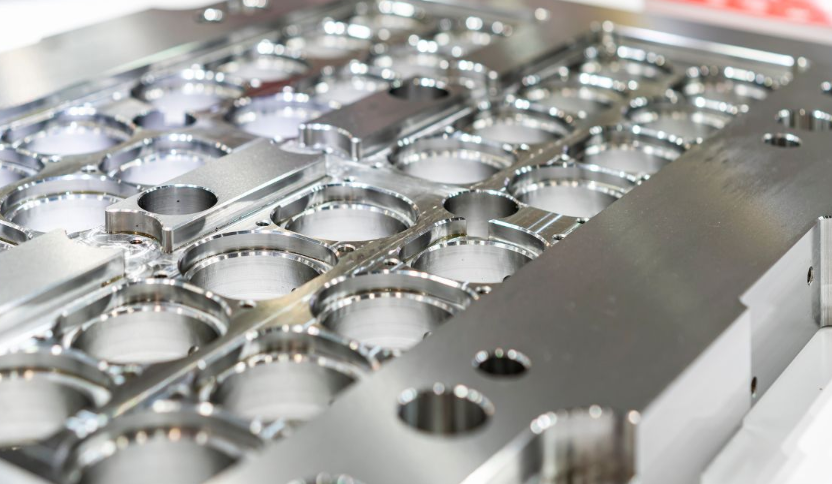
- CAD Modeling: Detailed 3D CAD models of the mold are created, including all necessary components such as cores, cavities, runners, gates, and cooling channels.
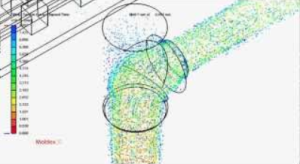
- Simulation and Analysis: Mold flow analysis software simulates the injection process to identify potential issues such as air traps, weld lines, and hotspots. Adjustments are made to optimize the design.
- Draft Angle: Design parts with appropriate draft angles to facilitate easy ejection from the mold.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
2. Material Selection
A. Mold Base Material
- Steel: Commonly used for its durability and ability to withstand high-volume production. Types include P20, H13, and stainless steel.
- Aluminum: Used for prototype or short-run molds due to its ease of machining and lower cost.
B. Components and Inserts
- Ejector Pins: Typically made from hardened steel to ensure durability.
- Cooling Channels: Designed and incorporated to ensure uniform cooling and minimize cycle time.
3. Machining and Fabrication
A. CNC Machining
- CNC Milling: High-precision CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling machines are used to create the mold cavities and cores. These machines follow the 3D CAD models to ensure accurate and consistent production.
- CNC Turning: Used for cylindrical components of the mold.
B. Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
- Wire EDM: Utilized for cutting intricate shapes and features that are difficult to machine using traditional methods.
- Sinker EDM: Used for creating detailed cavities and complex geometries in hardened steel molds.
C. Surface Finishing
- Polishing: Ensures a smooth finish on the mold surface, which is crucial for the quality of the final plastic part.
- Texturing: Applied to the mold surface to create specific textures or patterns on the molded part.
4. Assembly
A. Component Assembly
- Fitting and Alignment: All mold components, including cores, cavities, ejector systems, and cooling channels, are carefully assembled and aligned.
- Fastening: Components are securely fastened, ensuring there are no gaps or misalignments that could affect the mold’s performance.
B. Mold Testing
- Initial Testing: The assembled mold is tested with the injection molding machine to identify and correct any issues.
- Validation: Multiple test runs are conducted to ensure the mold produces parts that meet all design specifications and quality standards.
5. Quality Control
A. Dimensional Inspection
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine): Used to measure the dimensions of the mold cavities and components with high precision.
- Visual Inspection: Ensures there are no surface defects or misalignments.

As a leading mold injection manufacturer in China, we deliver superior molds for various industries. Our state-of-the-art facilities and expert team ensure top-notch quality and timely delivery. Contact us now for a competitive quote!
B. Performance Testing
- Trial Runs: Conducted to test the mold’s performance under actual production conditions. Parts are inspected for defects such as warpage, shrinkage, and surface finish.
- Cycle Time Analysis: Ensures the mold can produce parts within the required cycle time.
6. Finalization and Production
A. Mold Certification
- Documentation: Complete documentation of the mold design, materials used, and testing results.
- Approval: The mold is approved for mass production after meeting all quality and performance criteria.
B. Production Setup
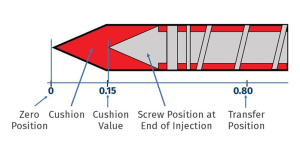
- Machine Setup: The mold is installed in the injection molding machine, and all necessary parameters (temperature, pressure, cycle time) are set.
- Production Run: The injection molding process begins, producing the required number of parts with consistency and efficiency.
Conclusion
The process of making injection molds for mass manufacturing is complex and requires precision at every stage. From initial design and material selection to machining, assembly, and quality control, each step is crucial to ensure the final mold meets the high standards required for large-scale production. Advanced technologies like CAD, CNC machining, and EDM play vital roles in achieving the precision and efficiency necessary for high-quality injection molding.
Related Conten: Plastic Blow Molding