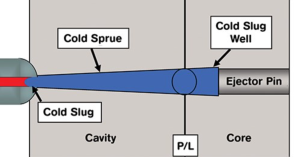
Cavity pressure in injection molding refers to the pressure within the mold cavity as the molten plastic is injected and fills the mold. This pressure is a critical parameter in the injection molding process because it directly affects the quality and consistency of the molded parts. Here’s a detailed look at what cavity pressure is, why it matters, and how it is managed in injection molding:
Definition and Importance of Cavity Pressure
Definition:
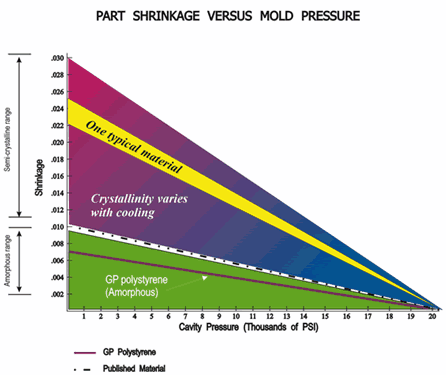
- Cavity Pressure: The pressure exerted by the molten plastic within the mold cavity during the injection molding cycle. It is measured at various stages, from the initial injection phase to the packing and cooling phases.
Importance:
- Quality Control: Proper management of cavity pressure ensures that parts are filled correctly without defects such as voids, sink marks, or incomplete fills.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Consistent cavity pressure helps maintain the dimensional accuracy and uniformity of the molded parts.
- Material Properties: Influences the mechanical properties and appearance of the final product, including surface finish and strength.
- Process Optimization: Monitoring and controlling cavity pressure allows for optimization of the injection molding process, reducing cycle times and improving efficiency.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Phases of Cavity Pressure
- Injection Phase:
- Initial Fill: Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity, rapidly increasing the cavity pressure.
- Flow Control: The pressure is managed to ensure smooth and complete filling of the cavity, avoiding turbulence and air entrapment.
- Packing Phase:
- Pressure Increase: After the cavity is filled, additional pressure is applied to pack more material into the mold, compensating for material shrinkage as it cools.
- Pressure Maintenance: Maintaining a steady cavity pressure during this phase ensures that the part has the correct density and reduces shrinkage-related defects.
- Cooling Phase:
- Pressure Decay: As the plastic cools and solidifies, the cavity pressure gradually decreases.
- Pressure Monitoring: Monitoring pressure during cooling helps ensure that the part retains its shape and dimensions as it solidifies.
Measuring and Controlling Cavity Pressure
Measurement:
- Sensors: Cavity pressure is measured using pressure sensors placed within the mold cavity. These sensors provide real-time data on the pressure during the injection molding cycle.
- Data Collection: The data collected by these sensors is used to analyze and optimize the molding process.
Control:
- Process Parameters: Adjusting injection speed, injection pressure, packing pressure, and cooling time based on cavity pressure readings ensures optimal filling and packing of the mold.
- Closed-Loop Control: Advanced injection molding machines use closed-loop control systems to automatically adjust process parameters in real-time, maintaining consistent cavity pressure throughout the cycle.
Benefits of Cavity Pressure Monitoring
- Defect Reduction: By maintaining optimal cavity pressure, defects such as flash, short shots, and sink marks can be minimized.
- Quality Consistency: Ensures consistent quality and dimensional accuracy across all parts produced in a production run.
- Process Optimization: Helps identify areas for process improvement, reducing cycle times and material waste.
- Troubleshooting: Provides valuable data for diagnosing and correcting issues in the molding process.
Conclusion
Cavity pressure is a vital aspect of the injection molding process that directly impacts the quality and consistency of molded parts. By accurately measuring and controlling cavity pressure, manufacturers can optimize their processes, reduce defects, and ensure high-quality production. Advanced monitoring and control systems play a crucial role in achieving these objectives, making cavity pressure management an essential practice in modern injection molding operations.
Related Conten: Plastic Blow Molding