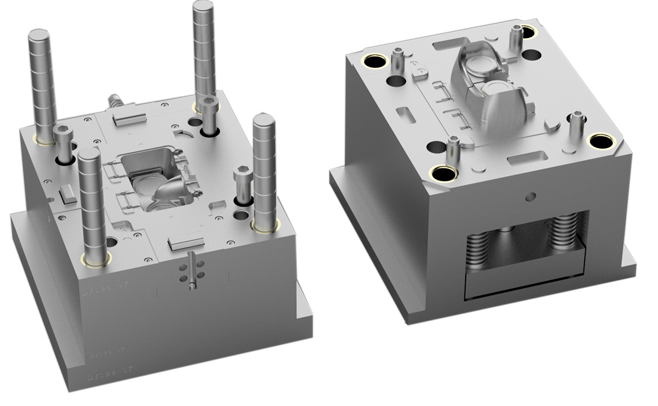
The lifespan of a tooled injection mold, often referred to as mold life or tool life, depends on several factors, including the type of material used for the mold, the design and complexity of the mold, the type of plastic being injected, the maintenance practices, and the production volume. Here’s a detailed breakdown of these factors and how they influence the longevity of an injection mold:
1. Mold Material
Steel Molds:
- Tool Steel (P20, H13, S7): These are commonly used for high-volume production molds. P20 steel molds can last between 50,000 to 100,000 cycles, while higher-grade steels like H13 and S7 can last 500,000 to 1,000,000 cycles or more with proper maintenance.
- Stainless Steel: Used for highly corrosive or abrasive materials, stainless steel molds can also last several hundred thousand cycles but are more expensive.
Aluminum Molds:
- General Purpose Aluminum: Suitable for low to medium-volume production, aluminum molds can typically last from 5,000 to 10,000 cycles.
- High-Grade Aluminum (e.g., QC-10): These can last up to 100,000 cycles but are still generally less durable than steel molds.
2. Mold Design and Complexity
Design Features:
- Simple Designs: Molds with fewer moving parts and simpler geometries tend to last longer because they are less prone to mechanical wear and tear.
- Complex Designs: Molds with intricate features, multiple slides, and cores will wear out more quickly due to the increased mechanical action and potential for higher stress concentrations.
3. Type of Plastic Material
Thermoplastics:
- Non-abrasive Materials (e.g., ABS, PP, PE): These materials are less harsh on the mold, contributing to longer mold life.
- Abrasive Materials (e.g., glass-filled nylons): These can significantly reduce mold life due to increased wear on the mold surfaces.
Thermosetting Plastics and Elastomers:
- Thermosetting Plastics: These often require molds that can withstand higher temperatures and pressures, which can reduce mold life.
- Elastomers: Similar to thermoplastics, the wear on the mold will depend on the specific properties of the elastomer used.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
4. Maintenance Practices
Regular Maintenance:
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Regular cleaning and lubrication of the mold components help prevent buildup of material and reduce wear on moving parts.
- Inspection and Repairs: Periodic inspections to identify and repair wear or damage can extend the mold’s lifespan.
Preventive Maintenance:
- Scheduled Downtime: Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule can help avoid unexpected failures and prolong mold life.
- Replacement of Worn Parts: Proactively replacing parts that show signs of wear before they fail completely can prevent damage to other parts of the mold.
5. Production Volume
High-Volume Production:
- Continuous Use: Molds used in high-volume production runs wear out faster due to constant use and exposure to thermal and mechanical stress.
Low to Medium-Volume Production:
- Intermittent Use: Molds used less frequently will naturally have a longer lifespan due to reduced exposure to stress.
Estimating Mold Life
Based on these factors, the estimated lifespan of a tooled injection mold can vary widely:
- Low-Volume Production Molds (Aluminum): 5,000 to 100,000 cycles.
- Medium-Volume Production Molds (P20 Steel): 50,000 to 100,000 cycles.
- High-Volume Production Molds (H13, S7 Steel): 500,000 to 1,000,000 cycles or more.

As a leading mold injection manufacturer in China, we deliver superior molds for various industries. Our state-of-the-art facilities and expert team ensure top-notch quality and timely delivery. Contact us now for a competitive quote!
Conclusion
The lifespan of a tooled injection mold is influenced by the mold material, design complexity, type of plastic material, maintenance practices, and production volume. While steel molds designed for high-volume production can last up to a million cycles or more, aluminum molds and molds used for lower volume production typically have a shorter lifespan. Proper maintenance and regular inspections are crucial to maximizing the life of any injection mold.
Related Conten: Quick Turn Injection Molding