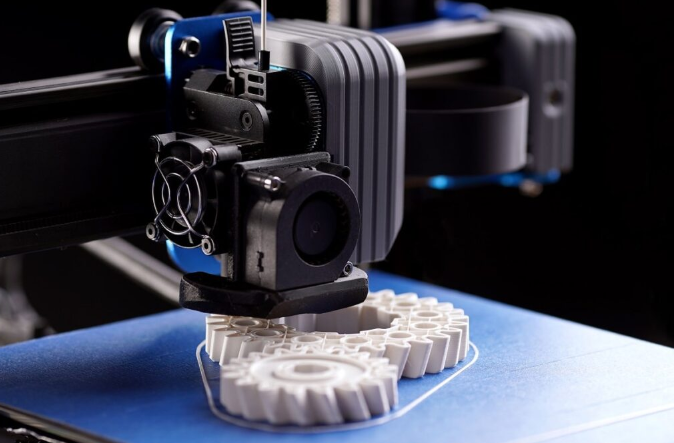
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. The creation of a 3D printed object is achieved using additive processes, where successive layers of material are laid down until the object is complete. Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced horizontal cross-section of the eventual object.
Key Steps in 3D Printing
- 3D Model Creation:
- The first step in 3D printing is creating a digital 3D model using computer-aided design (CAD) software or by scanning an existing object. The model is saved in a format like STL (stereolithography) or OBJ.
- Slicing the Model:
- The 3D model is then sliced into thin layers using slicing software. This software generates a G-code file, which instructs the 3D printer on how to build each layer.
- Printing Process:
- The 3D printer reads the G-code file and begins printing the object layer by layer. The printing material (such as plastic, metal, resin, or composite) is deposited by the printer’s nozzle or laser in the precise shape of each layer.
- Post-Processing:
- Once printing is complete, the object may require post-processing steps such as cleaning, sanding, or curing to achieve the desired finish and properties.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM):
- Uses a continuous filament of thermoplastic material. The filament is heated to its melting point and extruded layer by layer to create the object.
- Common materials: PLA, ABS, PETG.
- Stereolithography (SLA):
- Uses a UV laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic. The laser traces each layer of the object in the resin vat.
- Known for producing high-resolution and detailed prints.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):
- Uses a laser to sinter powdered material (usually nylon or other polymers), binding the material together to create a solid structure.
- Suitable for producing complex geometries and functional parts.
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) / Selective Laser Melting (SLM):
- Similar to SLS but uses metal powders. The laser melts the metal powder layer by layer to create strong and durable metal parts.
- Used in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP):
- Similar to SLA, but uses a digital light projector screen to flash a single image of each layer all at once, curing the resin.
- Faster than SLA and capable of producing highly detailed parts.
Applications of 3D Printing
- Prototyping:
- Rapid prototyping allows designers and engineers to quickly create and test their designs, accelerating the development process.
- Manufacturing:
- 3D printing can be used for low-volume production runs, custom manufacturing, and producing complex parts that are difficult to manufacture with traditional methods.
- Medical:
- Custom prosthetics, implants, and anatomical models for surgical planning are commonly produced using 3D printing.
- Aerospace:
- Lightweight and complex components for aircraft and spacecraft are created using high-strength materials like titanium and aluminum.
- Consumer Products:
- Custom and personalized products such as jewelry, clothing, and home goods can be manufactured on-demand with 3D printing.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Advantages of 3D Printing
- Design Flexibility: Ability to create complex geometries that are impossible or difficult with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Speed: Rapid production of prototypes and parts, reducing development time.
- Customization: Easy customization and personalization of products.
- Material Efficiency: Minimal waste compared to subtractive manufacturing processes.
References
- 3D Printing Industry: Comprehensive guide on different 3D printing processes and technologies.
- HowStuffWorks: Overview of 3D printing technology and its applications.
- Formlabs: Information on different 3D printing methods and materials.
3D printing continues to evolve and revolutionize manufacturing across various industries, offering new possibilities for design, production, and customization.
Related Conten: 3D Printing