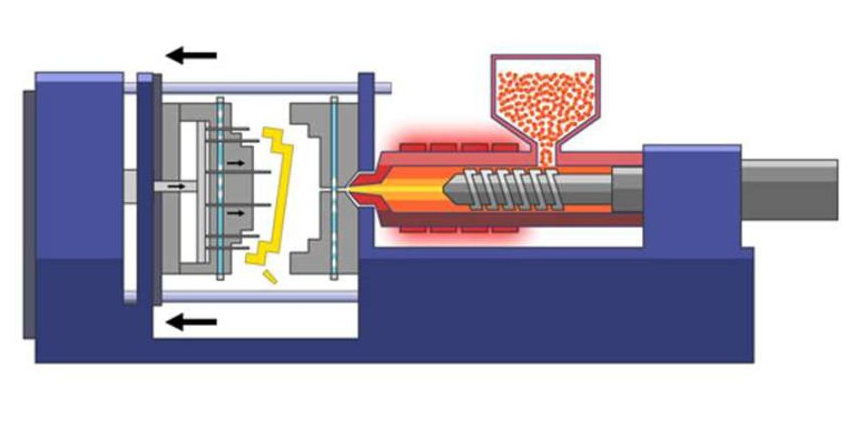
Plastic injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten plastic material into a mold. It is particularly popular for creating complex, high-precision parts in large volumes. Here’s a detailed look at what plastic injection molding entails:
Process Overview
- Clamping
- The process starts with the clamping unit, which holds the two halves of the mold securely together. The mold halves are typically made of metal, such as steel or aluminum, and are precision-machined to form the desired part shape. The clamping unit ensures the mold remains closed during the injection and cooling phases.
- Injection
- Plastic pellets, the raw material, are fed into the injection molding machine’s barrel. Inside the barrel, the pellets are heated until they melt. A screw or plunger then injects this molten plastic into the mold cavity through a nozzle. The injection process involves high pressure to ensure the mold is completely filled.
- Cooling
- Once the mold is filled, the plastic begins to cool and solidify, taking the shape of the mold cavity. Cooling time varies based on the material and the part’s geometry. The mold often has built-in cooling channels to expedite this process. Proper cooling is critical to prevent defects such as warping or shrinkage.
- Ejection
- After the part has sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the part is ejected by pins or other mechanisms. The part must be removed carefully to avoid damage. The mold can then be closed and ready for the next cycle.
- Post-Processing
- Once ejected, parts may require additional steps such as trimming excess material, surface finishing, painting, or assembly with other components. Quality inspection ensures that parts meet the required specifications.
Advantages of Plastic Injection Molding
- High Efficiency: The molding cycle is fast, allowing for the production of large quantities in a short time.
- Precision and Complexity: Capable of producing highly detailed and intricate parts with tight tolerances.
- Material Versatility: Compatible with a wide range of thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
- Automation: The process is highly automated, reducing labor costs and increasing repeatability and accuracy.
- Minimal Waste: Excess material can often be recycled and reused, leading to lower material waste.
Applications
Plastic injection molding is used across various industries, including:
- Automotive: Producing parts like dashboards, bumpers, and interior components.
- Consumer Goods: Manufacturing items such as toys, household products, and containers.
- Medical: Creating medical devices, syringes, and surgical instruments.
- Electronics: Making housings, connectors, and various electronic components.
[elementor-template id=”4330″]
Challenges
- High Initial Costs: Designing and manufacturing molds can be expensive, making the process less suitable for small production runs.
- Design Considerations: Parts must be designed with manufacturability in mind, including considerations for draft angles, wall thickness, and mold release.
- Material Limitations: Some plastics may require specific conditions to mold correctly or may not be suitable for injection molding.
Conclusion
Plastic injection molding is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process ideal for producing high-precision, complex parts in large quantities. Despite the high initial costs and design considerations, its advantages in terms of efficiency, precision, and material versatility make it a preferred method for many industries.
Related Conten: High Quality Prototype Plastic Injection Molding
 DTG Mould Trade Process |
|
| Quote: | According to sample, drawing and specific requirement. |
|---|---|
| Discussion | Mold material, cavity number, price, runner, payment, etc. |
| S/C Signature | Approval for all the items. |
| Advance | Pay 50% by T/T |
| Product Design Checking | We check the product design. If some position is not perfect, or can not be done on the mould, we will send customer the report. |
| Mold Processing | Send report to customer once each week |
| Mold Testing | Send trial samples and try-out report to customer for confirmation |
| Mold Modification | According to customer’s feedback. |
| Balance Settlement | 50% by T/T after the customer approved the trial sample and mould quality. |
| Delivery | Delivery by sea or air. The forwarder can be designated by your side. |
 |
|
