In injection molding, various components and mechanisms are used to connect, align, and secure different parts of the mold to ensure proper function and high-quality production. Here are the key elements that connect and hold the pieces of an injection mold together:
1. Clamping Units:
- Purpose: Clamping units are integral parts of the injection molding machine that hold the mold halves (core and cavity) together with sufficient force to counteract the pressure of the molten plastic being injected.
- Mechanism: They use hydraulic or mechanical force to keep the mold halves securely closed during the injection and cooling phases.
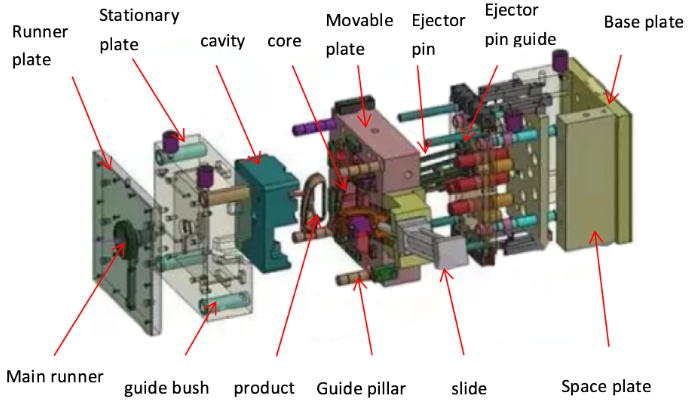
2. Guide Pins and Bushings:
- Purpose: Guide pins and bushings ensure precise alignment of the mold halves, preventing misalignment that can lead to defects or damage.
- Mechanism: Guide pins, typically located on one half of the mold, fit into bushings on the other half to maintain proper alignment.
3. Ejector System:
- Purpose: The ejector system removes the finished part from the mold after it has cooled and solidified.
- Components: Ejector pins, plates, and rods work together to push the molded part out of the mold cavity.
- Mechanism: Ejector pins are activated by the ejector plate, which is driven by the machine’s ejector mechanism or hydraulic cylinders.
4. Sprue, Runner, and Gate System:
- Purpose: These components channel the molten plastic from the injection molding machine nozzle to the mold cavities.
- Components:
- Sprue: The main channel through which the molten plastic enters the mold.
- Runners: Channels that distribute the molten plastic to various cavities in multi-cavity molds.
- Gates: Small openings through which the plastic enters the mold cavity.
- Mechanism: Proper design and placement of these components are crucial for ensuring balanced flow and minimizing defects.
5. Cooling Channels:
- Purpose: Cooling channels circulate coolant (usually water) to remove heat from the mold, ensuring that the plastic solidifies uniformly and quickly.
- Mechanism: Cooling channels are strategically placed within the mold to optimize heat removal and minimize cycle time.
6. Bolts and Fasteners:
- Purpose: Bolts and fasteners are used to secure mold components and plates together.
- Mechanism: They provide structural integrity and maintain alignment and stability during the injection molding process.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
7. Leader Pins:
- Purpose: Leader pins help in the precise alignment of mold halves and ensure smooth opening and closing of the mold.
- Mechanism: Leader pins are located on one half of the mold and fit into corresponding holes or bushings on the other half.
8. Interlocks:
- Purpose: Interlocks ensure precise alignment and prevent shifting of mold components during operation.
- Mechanism: They provide additional support and alignment, particularly in complex molds with multiple moving parts.
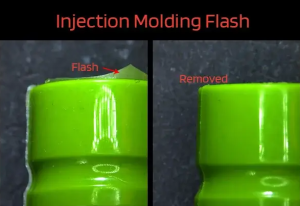
9. Parting Line:
- Purpose: The parting line is the interface where the mold halves meet and separate.
- Mechanism: Proper design and maintenance of the parting line are essential for minimizing flash and ensuring the integrity of the molded part.
Conclusion
In injection molding, connecting and securing the various pieces of the mold is crucial for producing high-quality parts. Components like clamping units, guide pins, ejector systems, sprue and runner systems, cooling channels, bolts and fasteners, leader pins, and interlocks work together to ensure proper alignment, stability, and efficient operation of the mold. Understanding the function and importance of these elements helps in optimizing the injection molding process and achieving consistent, defect-free production.
Related Conten: High Quality Prototype Plastic Injection Molding