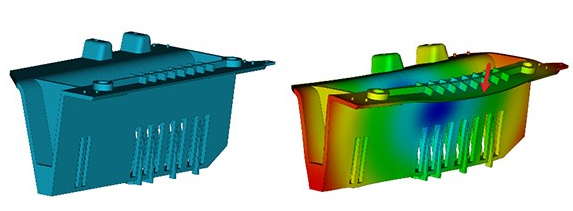
Warping is a common defect in injection molded parts, where the part bends or twists out of shape after cooling. This deformation occurs due to uneven shrinkage during the cooling process and can significantly impact the functionality and aesthetics of the final product. Understanding the causes of warping and implementing strategies to prevent it is crucial for producing high-quality injection molded parts.
Primary Causes of Warping in Injection Molding
- Uneven Cooling:
- When different areas of the part cool at different rates, it leads to differential shrinkage, causing the part to warp.
- Non-Uniform Wall Thickness:
- Parts with varying wall thicknesses cool unevenly, leading to warping as thicker sections shrink more than thinner ones.
- Material Selection:
- Some materials have higher shrinkage rates or are more prone to warping due to their molecular structure and thermal properties.
- Mold Design Issues:
- Poor mold design, including inadequate cooling channels or improper gate placement, can result in uneven cooling and warping.
- High Injection Pressure:
- Excessive injection pressure can lead to high residual stresses in the part, causing it to warp during cooling.
- Improper Packing Pressure:
- Inadequate or excessive packing pressure can result in uneven shrinkage and warping of the part.
- Inadequate Mold Temperature:
- If the mold temperature is not properly controlled, it can cause differential cooling and shrinkage, leading to warping.
- Orientation Effects:
- During injection molding, the polymer molecules can become oriented in the direction of flow. Upon cooling, the relaxation of these oriented molecules can cause warping.
Preventing Warping in Injection Molding
- Ensure Uniform Cooling:
- Design the mold with efficient and uniform cooling channels to promote even cooling of the part.
- Design for Uniform Wall Thickness:
- Avoid drastic changes in wall thickness to ensure even cooling and reduce differential shrinkage.
- Select Appropriate Materials:
- Choose materials with low shrinkage rates and good dimensional stability to minimize warping.
- Optimize Mold Design:
- Properly place gates and design the mold to facilitate even filling and cooling. Consider using conformal cooling channels for better thermal management.
- Control Injection Pressure:
- Adjust injection pressure to appropriate levels to minimize residual stresses in the part.
- Optimize Packing Pressure:
- Ensure the packing pressure is sufficient to compensate for material shrinkage without causing excessive stress.
- Regulate Mold Temperature:
- Maintain consistent mold temperatures to promote uniform cooling and reduce the risk of warping.
- Manage Orientation Effects:
- Optimize the injection process parameters, such as injection speed and pressure, to minimize molecular orientation and its effects on warping.
- Use Mold Flow Analysis:
- Employ mold flow simulation software to predict and address potential warping issues before actual production.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Conclusion
Warping in injection molded parts can lead to significant quality issues, affecting both the functionality and appearance of the final product. By understanding the primary causes of warping, such as uneven cooling, non-uniform wall thickness, material selection, and mold design issues, manufacturers can take proactive steps to prevent this defect. Implementing strategies like ensuring uniform cooling, designing for consistent wall thickness, selecting appropriate materials, and optimizing injection parameters will help minimize warping and ensure the production of high-quality, dimensionally stable injection molded parts.
Related Conten: Injection Molding Factory