Extrusion and injection molding are two widely used manufacturing processes in the plastics industry, each suited to different applications and product types. Both methods involve the shaping of plastic materials through the application of heat and pressure, but they differ significantly in their processes, applications, and advantages. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate method for specific manufacturing needs.
Extrusion
Process
Extrusion involves pushing melted plastic through a shaped die to create continuous lengths of a specific cross-sectional profile. The process includes the following steps:
- Feeding: Plastic pellets or granules are fed into a hopper.
- Melting: The plastic is heated and melted as it is conveyed through a heated barrel by a rotating screw.
- Shaping: The molten plastic is forced through a die, which shapes it into the desired continuous profile.
- Cooling: The shaped plastic is cooled, usually by passing through a water bath or air cooling.
- Cutting: The continuous plastic profile is cut into desired lengths if necessary.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Applications
Extrusion is commonly used for producing items with a constant cross-sectional profile, such as:
- Pipes and tubes
- Sheets and films
- Profiles and moldings
- Wire and cable insulation
Advantages
- Continuous Production: Ideal for producing long lengths of material.
- Efficiency: High production rates and minimal material wastage.
- Cost-Effective: Economical for large-scale production of simple shapes.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of materials and product types.
Injection Molding
Process
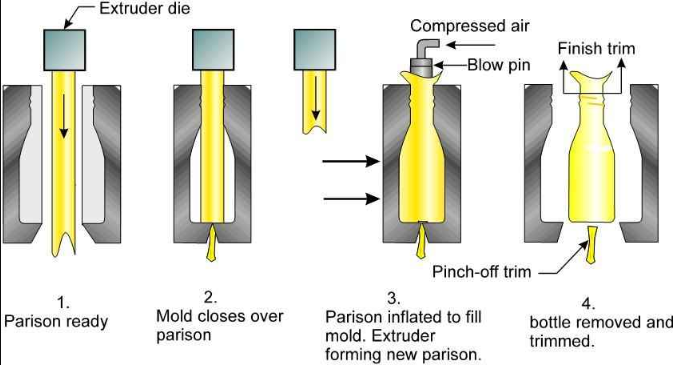
Injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity to create discrete parts. The process includes the following steps:
- Feeding: Plastic pellets or granules are fed into a hopper.
- Melting: The plastic is heated and melted in a heated barrel.
- Injection: The molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure.
- Cooling: The plastic solidifies in the mold as it cools.
- Ejection: The solidified part is ejected from the mold.
Applications
Injection molding is commonly used for producing complex, detailed parts in high volumes, such as:
- Automotive components
- Consumer electronics housings
- Medical devices
- Toys and household items
Advantages
- Complex Geometries: Capable of producing intricate and detailed parts.
- High Precision: Consistent and high-quality parts with tight tolerances.
- High Volume Production: Efficient for mass production of identical parts.
- Material Versatility: Can use a wide range of plastic materials, including those with fillers and additives.

As a leading mold injection manufacturer in China, we deliver superior molds for various industries. Our state-of-the-art facilities and expert team ensure top-notch quality and timely delivery. Contact us now for a competitive quote!
Key Differences
1. Product Types
- Extrusion: Produces continuous profiles with constant cross-sections.
- Injection Molding: Produces discrete, complex parts with detailed geometries.
2. Process Flow
- Extrusion: Continuous process, where the product is created in a continuous length and cut to size as needed.
- Injection Molding: Cyclical process, where each cycle produces a single or multiple discrete parts.
3. Tooling
- Extrusion: Uses a die to shape the plastic, which is simpler and generally less expensive than molds used in injection molding.
- Injection Molding: Uses a mold cavity, which can be complex and expensive to produce, but allows for high precision and detailed parts.
4. Production Efficiency
- Extrusion: Highly efficient for producing large quantities of simple shapes continuously.
- Injection Molding: Highly efficient for producing large quantities of complex parts quickly.
5. Material Usage
- Extrusion: Generally produces less material waste as it creates continuous profiles.
- Injection Molding: May have more material wastage due to the sprue, runners, and gates, but this can often be recycled.
6. Flexibility
- Extrusion: Best suited for products requiring uniform cross-sections.
- Injection Molding: Highly flexible for producing parts with intricate designs and varying thicknesses.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Conclusion
Both extrusion and injection molding are vital processes in the plastics industry, each with its unique strengths and applications. Extrusion is ideal for creating continuous profiles and products with uniform cross-sections, while injection molding excels in producing complex, detailed parts with high precision and consistency. Selecting the appropriate method depends on the specific requirements of the product, including its design, volume, and material considerations. By understanding the differences between these processes, manufacturers can make informed decisions to achieve optimal production efficiency and product quality.
Related Conten: Custom Plastic Extrusions