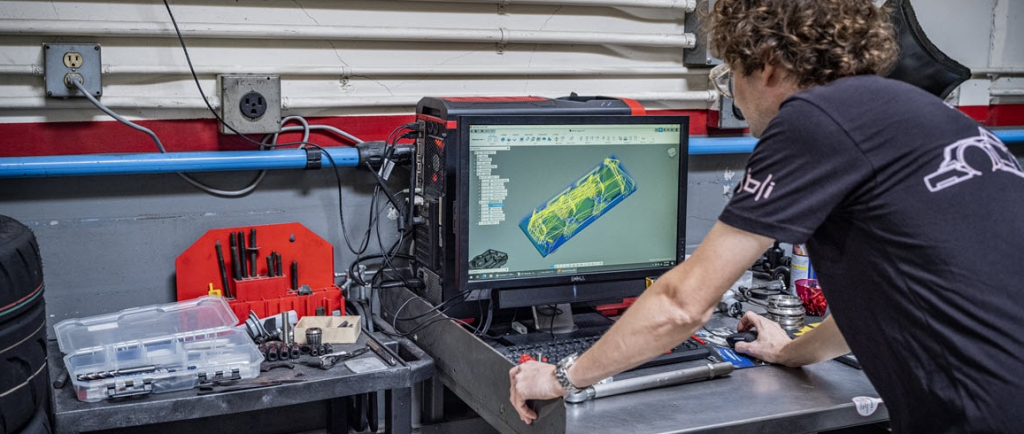
CNC programming is an essential component of modern manufacturing, enabling the precise control of machine tools to produce complex parts and components. This article will explore what CNC programming is, its benefits, applications, and key considerations for those looking to leverage this technology in their operations. By understanding these aspects, you can optimize your manufacturing processes and achieve superior results.
What is CNC Programming?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) programming involves creating a set of instructions that a CNC machine follows to perform various machining operations. These instructions, written in a specific programming language such as G-code, dictate the movements of the machine’s tools, the speed and feed rates, and other parameters required to manufacture a part.
Benefits of CNC Programming
- High Precision and Accuracy
- Tight Tolerances: CNC programming enables machines to achieve extremely tight tolerances, essential for high-precision applications.
- Consistent Quality: Automated control ensures consistent quality across multiple parts, reducing the risk of human error.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity
- Automated Operations: CNC machines can run continuously and perform complex tasks without constant human supervision, increasing throughput.
- Reduced Setup Time: Once a program is created, it can be reused, significantly reducing setup time for subsequent operations.
- Versatility
- Wide Range of Operations: CNC programming supports various machining operations, including milling, turning, drilling, and grinding.
- Complex Geometries: Capable of producing intricate shapes and complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible with manual machining.
- Cost-Effective Production
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automation reduces the need for skilled labor, lowering overall production costs.
- Minimized Waste: Precision machining minimizes material waste, further reducing costs.
Applications of CNC Programming
- Aerospace Industry
- Precision Components: Manufacturing of precision components such as turbine blades, aircraft structural parts, and engine components.
- Complex Assemblies: Production of complex assemblies that require high precision and tight tolerances.
- Automotive Industry
- Engine Parts: Creation of engine components, transmission parts, and other automotive parts.
- Prototyping: Rapid prototyping of new designs and components.
- Medical Industry
- Surgical Instruments: Manufacturing of surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics with high precision.
- Dental Applications: Production of dental crowns, bridges, and other dental appliances.
- Consumer Goods
- Custom Products: Creation of custom and high-end consumer products such as jewelry, watches, and electronics.
- Home Appliances: Production of components for home appliances and other consumer electronics.

As a leading mold injection manufacturer in China, we deliver superior molds for various industries. Our state-of-the-art facilities and expert team ensure top-notch quality and timely delivery. Contact us now for a competitive quote!
Key Considerations for CNC Programming
- Programming Languages
- G-code: The most widely used CNC programming language, consisting of a series of commands that control machine operations.
- CAM Software: Advanced CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software can generate G-code from CAD models, simplifying the programming process.
- Machine Capabilities
- Axes and Movements: Ensure the CNC machine’s capabilities align with the requirements of the part being manufactured.
- Tooling and Accessories: Select appropriate tooling and accessories based on the material and machining operations.
- Simulation and Testing
- Program Verification: Run simulations to verify the CNC program and identify potential issues before actual production.
- Test Runs: Conduct test runs on less expensive materials to ensure the program performs as expected.
- Operator Training
- Skilled Workforce: Employ skilled operators trained in CNC programming and machining techniques.
- Continuous Training: Provide ongoing training to keep operators updated with the latest technologies and methodologies.
Future Trends in CNC Programming
- Advanced CAM Software
- Automated Programming: Development of CAM software that can automatically generate optimized CNC programs from CAD models.
- AI Integration: Integration of artificial intelligence to enhance program optimization and adapt to real-time machining conditions.
- Enhanced Connectivity
- IoT Integration: Connecting CNC machines to the Internet of Things (IoT) for real-time monitoring, data collection, and predictive maintenance.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Use of cloud-based platforms for remote programming, monitoring, and control of CNC machines.
- Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
- Green Manufacturing: Adoption of eco-friendly practices and materials to reduce the environmental impact of CNC machining.
- Energy-Efficient Machines: Development of energy-efficient CNC machines that consume less power and reduce operational costs.
Conclusion
CNC programming is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility. Its applications span across various industries, from aerospace and automotive to medical and consumer goods. By understanding the benefits and key considerations of CNC programming, manufacturers can optimize their processes, reduce costs, and achieve superior results. As the technology continues to evolve, embracing these advancements will be key to staying competitive in the ever-changing manufacturing landscape.
Related Conten: https://www.m-dtg.com/service/mold-manufacturing/