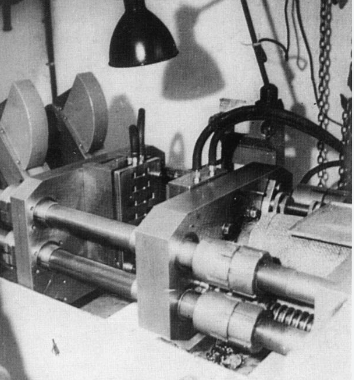
Injection molding, a pivotal manufacturing process in the plastics industry, was invented in 1872 by American inventor John Wesley Hyatt and his brother Isaiah Hyatt. The Hyatts’ invention marked the beginning of modern plastic manufacturing, enabling the mass production of complex plastic parts with high precision and efficiency.
The Invention of Injection Molding
Background
John Wesley Hyatt was already known for his work with celluloid, the first thermoplastic, which he developed as a substitute for ivory in billiard balls. His experimentation with celluloid led him to seek a method to shape the material efficiently and consistently. This quest resulted in the creation of the first injection molding machine.
The First Injection Molding Machine
The first injection molding machine invented by the Hyatt brothers was relatively simple compared to today’s advanced machines. It consisted of a basic plunger that injected plastic into a mold through a heated cylinder. This invention allowed for the creation of small, intricate parts that were difficult to produce with traditional manufacturing methods.
Early Applications
The initial applications of injection molding were limited, focusing primarily on simple items like buttons, combs, and dental products. However, the potential for more complex and diverse applications quickly became apparent as the technology evolved.
[elementor-template id=”4330″]
Evolution and Development
20th Century Advances
The injection molding process saw significant advancements throughout the 20th century. Key developments included:
- 1920s: The introduction of more sophisticated molds and the use of thermoplastic materials expanded the range of possible applications.
- 1940s-1950s: World War II drove the demand for mass-produced plastic parts, leading to significant advancements in injection molding technology. This period saw the introduction of hydraulic machines, which provided more precise control over the molding process.
- 1970s: The advent of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) revolutionized mold design and production, enabling more complex and precise parts.
Modern Injection Molding
Today, injection molding is a highly automated and sophisticated process capable of producing intricate and high-precision parts in large volumes. Modern machines use advanced control systems, robotics, and high-performance materials to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and quality.
Key Technological Milestones
- Introduction of Thermoplastics: The development of new thermoplastic materials expanded the range of applications for injection molding, from automotive parts to medical devices.
- Electric Injection Molding Machines: These machines offer greater energy efficiency, precision, and speed compared to traditional hydraulic machines.
- Micro Injection Molding: This technology enables the production of extremely small and precise parts, catering to industries like electronics and medical devices.
[elementor-template id=”4331″]
Impact and Significance
Injection molding has had a profound impact on manufacturing and product design, enabling the mass production of complex plastic parts that are essential in various industries, including automotive, electronics, consumer goods, and medical devices. Its ability to produce high-quality, cost-effective components has made it a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Benefits
- High Efficiency: Injection molding allows for the rapid production of large quantities of parts with consistent quality.
- Precision and Complexity: The process can produce intricate and detailed parts with high accuracy, which would be challenging or impossible with other manufacturing methods.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Once the initial mold is created, the cost per part is relatively low, making it ideal for high-volume production.
Conclusion
Since its invention by John Wesley Hyatt and Isaiah Hyatt in 1872, injection molding has undergone significant advancements, transforming into a critical technology in modern manufacturing. Its ability to efficiently produce high-quality, complex plastic parts has made it indispensable in various industries, continually driving innovation and development in product design and manufacturing processes.
Related Conten: Industrial Molds
 DTG Mould Trade Process |
|
| Quote: | According to sample, drawing and specific requirement. |
|---|---|
| Discussion | Mold material, cavity number, price, runner, payment, etc. |
| S/C Signature | Approval for all the items. |
| Advance | Pay 50% by T/T |
| Product Design Checking | We check the product design. If some position is not perfect, or can not be done on the mould, we will send customer the report. |
| Mold Processing | Send report to customer once each week |
| Mold Testing | Send trial samples and try-out report to customer for confirmation |
| Mold Modification | According to customer’s feedback. |
| Balance Settlement | 50% by T/T after the customer approved the trial sample and mould quality. |
| Delivery | Delivery by sea or air. The forwarder can be designated by your side. |
 |
|

