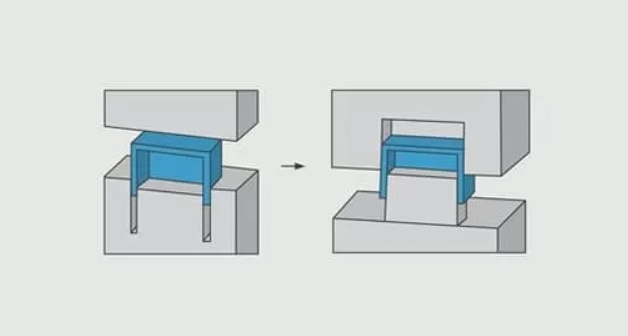
In injection molding, the terms “core” and “cavity” refer to the two halves of the mold that come together to form the mold cavity where the plastic part is shaped. Each half plays a specific role in forming the final part and is critical to the mold’s function and the quality of the molded product.
Core
- Definition: The core is the half of the mold that forms the internal surfaces of the part. It typically has protrusions and features that shape the internal details of the molded product.
- Location: The core is usually the moving half of the mold, attached to the injection molding machine’s moving platen, which allows for the opening and closing of the mold.
- Function: The core forms the interior features of the part, such as holes, recesses, and undercuts. It is designed to be withdrawn from the molded part during the ejection phase of the cycle.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Cavity
- Definition: The cavity is the half of the mold that forms the external surfaces of the part. It typically has a hollow space that matches the desired outer shape of the final product.
- Location: The cavity is usually the stationary half of the mold, attached to the injection molding machine’s stationary platen.
- Function: The cavity forms the exterior features of the part. It is designed to shape the outer dimensions and surface finishes of the molded product.
Core and Cavity Interaction
- Mold Assembly: When the mold closes, the core and cavity halves come together to form the complete mold cavity, the hollow space where the plastic is injected and shaped.
- Injection Process: Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity through the gate and runner system. The plastic fills the space between the core and cavity, taking on the shape of the cavity’s interior and the core’s exterior.
- Cooling and Solidification: After the plastic fills the cavity, it is allowed to cool and solidify. Cooling channels in the mold help regulate the temperature to ensure proper solidification and part quality.
- Ejection: Once the part has solidified, the mold opens, and the core is retracted, allowing the part to be ejected. Ejector pins or other mechanisms help push the part off the core.
Design Considerations
- Precision and Alignment: The core and cavity must be precisely machined and aligned to ensure that the parts produced meet tight tolerances and specifications.
- Surface Finish: The quality of the surfaces of the core and cavity will directly affect the surface finish of the molded part. Polished surfaces can improve the finish, while textured surfaces can create desired textures on the part.
- Cooling Efficiency: The design of cooling channels in both the core and cavity is crucial for efficient heat removal, reducing cycle time, and ensuring consistent part quality.
- Material Selection: The materials used for the core and cavity must be durable enough to withstand the pressures and temperatures of the injection molding process. Common materials include hardened steel, stainless steel, and sometimes aluminum for prototype molds.
Examples of Core and Cavity Applications
- Simple Parts: For simple parts like a basic plastic cap, the core forms the interior hollow and threading, while the cavity forms the outer shape and surface.
- Complex Parts: For more complex parts with intricate internal features, such as a plastic container with built-in supports or ribs, the core and cavity must be designed to include these details.
- Multi-cavity Molds: In multi-cavity molds, there are multiple core and cavity pairs within the same mold base, allowing for the production of multiple parts in a single cycle.

As a leading mold injection manufacturer in China, we deliver superior molds for various industries. Our state-of-the-art facilities and expert team ensure top-notch quality and timely delivery. Contact us now for a competitive quote!
Summary
The core and cavity are essential components of an injection mold, working together to form the mold cavity where the plastic part is shaped. The core forms the internal features, while the cavity forms the external surfaces of the part. Proper design and alignment of the core and cavity are crucial for producing high-quality, consistent molded parts efficiently.
Related Conten: https://www.m-dtg.com/landing-page/custom-plastic-extrusions/