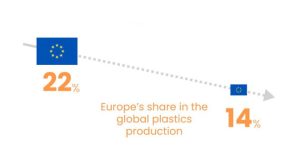
A CNC programmer is a skilled professional who creates the instructions that CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines follow to perform tasks such as cutting, drilling, milling, and shaping materials. They play a crucial role in the manufacturing process, ensuring that parts and components are produced accurately and efficiently. Here’s an in-depth look at what a CNC programmer does, their skills, and their importance in the industry:
Roles and Responsibilities of a CNC Programmer
- Design Interpretation
- Reading Technical Drawings: Interprets blueprints, technical drawings, and CAD (Computer-Aided Design) models to understand the specifications of the part to be manufactured.
- Identifying Requirements: Determines dimensions, tolerances, materials, and other critical factors necessary for production.
- Programming
- G-code Creation: Develops G-code, the programming language used by CNC machines, to direct the machine’s movements and operations.
- CAM Software Usage: Utilizes CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software to generate toolpaths and convert CAD models into machine-readable instructions.
- Toolpath Optimization: Ensures efficient toolpaths to minimize machining time and material waste while maintaining precision and quality.
- Machine Setup and Troubleshooting
- Machine Configuration: Sets up CNC machines by loading the program, installing the appropriate tools, and positioning the workpiece.
- Simulation and Testing: Runs simulations to verify the program’s accuracy and makes adjustments as needed.
- Problem Solving: Diagnoses and resolves issues that arise during the programming or machining process to ensure smooth operation.
- Quality Control
- Inspection and Verification: Inspects the finished parts to ensure they meet the required specifications and quality standards.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously refines programs and processes to improve efficiency, accuracy, and overall performance.
Essential Skills for a CNC Programmer
- Technical Proficiency
- CAD/CAM Software: Proficient in using CAD software for design and CAM software for generating CNC programs.
- G-code Knowledge: Deep understanding of G-code and other relevant programming languages.
- Machining Knowledge
- Understanding of Materials: Knowledge of different materials (metals, plastics, composites) and their properties.
- Tool Selection: Ability to select appropriate cutting tools and machine settings for various tasks.
- Problem-Solving Skills
- Analytical Thinking: Ability to troubleshoot issues and make necessary adjustments to programs and machine settings.
- Attention to Detail: Ensures accuracy in programming and machining to produce high-quality parts.
- Communication Skills
- Collaboration: Works closely with designers, engineers, and machinists to understand requirements and ensure successful production.
- Documentation: Maintains detailed records of programs, machine settings, and troubleshooting steps.
Importance of a CNC Programmer
- Precision and Accuracy
- CNC programmers ensure that parts are manufactured to exact specifications, maintaining high quality and consistency.
- Efficiency
- By optimizing toolpaths and machining processes, CNC programmers reduce production time and material waste, increasing overall efficiency.
- Customization and Flexibility
- They enable the production of complex and customized parts that meet specific requirements, supporting diverse manufacturing needs.
- Cost Savings
- Efficient programming reduces downtime, material costs, and the need for rework, contributing to cost-effective production.
Conclusion
A CNC programmer is an essential figure in modern manufacturing, bridging the gap between design and production. Their expertise in programming, machining, and problem-solving ensures that CNC machines operate efficiently and produce high-quality parts. As technology advances, the role of a CNC programmer continues to evolve, requiring ongoing learning and adaptation to new tools and techniques.
Related Conten: Quick Turn Injection Molding