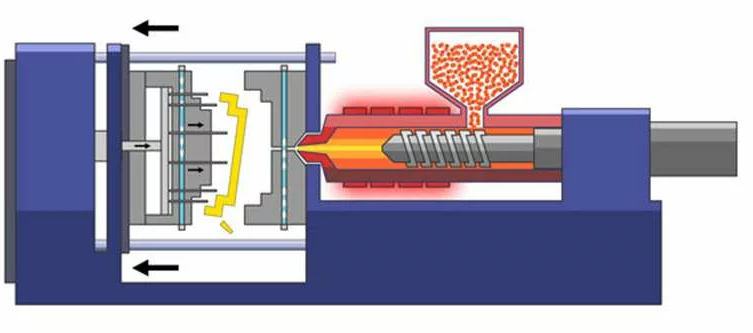
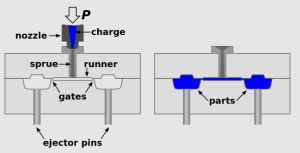
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce plastic parts in large volumes. It involves injecting molten plastic into a mold where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how injection molding is done:
Step-by-Step Injection Molding Process
- Material Preparation:
- Plastic pellets (the raw material) are dried to remove moisture, which can cause defects in the final part.
- Feeding:
- The dried plastic pellets are fed from a hopper into the barrel of the injection molding machine.
- Plasticizing:
- Inside the barrel, a rotating screw moves the pellets forward. The pellets are heated by external heaters and by friction as they are pushed forward by the screw, turning them into molten plastic.
- Injection:
- Once enough plastic has melted, the screw moves forward, acting like a plunger, and injects the molten plastic through the nozzle into the mold cavity at high pressure.
- Packing and Holding:
- After the initial injection, the screw maintains pressure (packing) to ensure the mold cavity is completely filled and to compensate for any shrinkage as the plastic begins to cool.
- Cooling:
- The mold, equipped with cooling channels, circulates coolant (typically water) to cool the molten plastic and solidify it into the shape of the mold cavity. Cooling time depends on the part’s thickness and the efficiency of the cooling system.
- Mold Opening:
- Once the plastic part has sufficiently cooled and solidified, the clamping unit opens the mold, separating the two halves.
- Ejection:
- The ejection system, which may include ejector pins, plates, or air blasts, pushes the cooled part out of the mold.
- Part Removal:
- The part is removed from the ejection area and inspected for any defects. It may also undergo post-processing like trimming, deburring, or painting.
- Cycle Repeat:
- The mold closes, and the process repeats for the next cycle.
Key Components and Their Roles
- Hopper:
- Holds and feeds the plastic pellets into the barrel.
- Barrel:
- Heats and melts the plastic pellets.
- Screw:
- Rotates to move and melt the plastic pellets and acts as a plunger during the injection phase.
- Nozzle:
- Directs the molten plastic into the mold.
- Mold:
- Consists of two halves (core and cavity) that shape the final part. It includes cooling channels to help solidify the plastic quickly.
- Clamping Unit:
- Opens and closes the mold and holds it shut during injection and cooling.
- Ejector System:
- Removes the finished part from the mold after it cools.
Considerations for Quality Injection Molding
- Material Selection:
- Choose the right plastic material based on the part’s requirements (e.g., strength, flexibility, heat resistance).
- Mold Design:
- Design the mold to ensure proper filling, cooling, and ejection. Consider the placement of gates, runners, cooling channels, and ejector pins.
- Machine Settings:
- Optimize temperature, pressure, injection speed, and cooling time to produce high-quality parts consistently.
- Quality Control:
- Regularly inspect and test parts to ensure they meet specifications. Address any defects such as warping, sink marks, or voids.
- Maintenance:
- Regular maintenance of the injection molding machine and molds is essential to ensure consistent production quality and extend the equipment’s lifespan.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Common Defects and Solutions
- Warping:
- Solution: Optimize cooling rates, ensure uniform wall thickness, and adjust mold temperature.
- Sink Marks:
- Solution: Increase packing pressure, adjust cooling time, and ensure adequate gate size.
- Voids:
- Solution: Increase injection pressure, optimize mold temperature, and ensure proper venting.
- Flash:
- Solution: Check mold clamping pressure, ensure mold alignment, and adjust injection speed.
- Short Shots:
- Solution: Increase injection pressure, ensure proper venting, and adjust melt temperature.
Conclusion
Injection molding is a versatile and efficient process for producing large volumes of plastic parts with high precision. It involves several steps, from preparing and injecting molten plastic into a mold to cooling and ejecting the finished part. Proper material selection, mold design, machine settings, and quality control are essential for producing high-quality injection-molded parts. Regular maintenance of the injection molding machine and molds ensures consistent production and longevity of the equipment.
Related Conten: Plastic Assembly Decoration