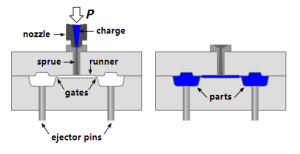
Injection molds are complex tools that are essential for the injection molding process. They are designed to form molten plastic into specific shapes as it cools and solidifies. The process of making injection molds involves several steps, from initial design to final production. Here’s an in-depth look at how injection molds are made:
1. Design
A. Concept and Part Design:
- The first step is to create a detailed design of the part to be produced. This involves understanding the part’s specifications, including dimensions, material, and functionality.
B. Mold Design:
- Based on the part design, a mold design is created. This includes designing the core and cavity, the gating system (through which the plastic enters the mold), the ejection system, cooling channels, and any necessary sliders or lifters.
C. CAD Software:
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software is used to create a precise 3D model of the mold. This allows for detailed visualization and simulation of the mold and the molding process.
2. Material Selection
A. Mold Base:
- The mold base is typically made from steel or aluminum. Steel is more durable and can withstand higher pressures and temperatures, while aluminum is easier to machine and cools faster.
B. Core and Cavity:
- The core and cavity, which form the shape of the part, are usually made from high-quality tool steel to ensure durability and precision.
3. Machining
A. CNC Machining:
- Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are used to precisely cut and shape the mold components. CNC machining ensures high accuracy and repeatability.
B. EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining):
- EDM is used for creating intricate details and complex geometries that are difficult to achieve with traditional machining. It involves using electrical discharges to erode material.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
4. Heat Treatment
A. Hardening:
- The mold components, especially those made from steel, are often heat-treated to increase their hardness and durability. This involves heating the steel to a high temperature and then cooling it rapidly.
B. Tempering:
- After hardening, the steel is tempered to relieve internal stresses and improve toughness. This involves reheating the steel to a lower temperature and then cooling it slowly.
5. Surface Finishing
A. Polishing:
- The mold surfaces, especially the cavity and core, are polished to achieve a smooth finish. This is important for producing parts with a high-quality surface finish.
B. Texturing:
- If the part requires a specific surface texture, the mold surfaces can be textured using chemical etching or laser engraving.
6. Assembly
A. Fitting:
- The individual mold components are carefully fitted together to ensure proper alignment and function. This includes assembling the core and cavity, the gating system, ejection system, and cooling channels.
B. Testing:
- The assembled mold is tested by performing trial runs. This helps identify any issues with the mold design or machining that need to be corrected.
7. Final Adjustments
A. Tuning:
- Based on the results of the trial runs, final adjustments are made to the mold to ensure it produces parts that meet the required specifications. This may involve fine-tuning the dimensions, adjusting the cooling channels, or modifying the gating system.
B. Quality Control:
- The mold undergoes rigorous quality control checks to ensure it meets all design and performance criteria. This includes checking the dimensions, surface finish, and overall functionality.

As a leading mold injection manufacturer in China, we deliver superior molds for various industries. Our state-of-the-art facilities and expert team ensure top-notch quality and timely delivery. Contact us now for a competitive quote!
8. Production
A. Mass Production:
- Once the mold is finalized and approved, it is used for mass production. The mold is mounted on an injection molding machine, where molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity, cooled, and ejected as finished parts.
B. Maintenance:
- Regular maintenance is essential to keep the mold in good working condition. This includes cleaning, lubrication, and periodic inspections to identify and address any wear or damage.
Conclusion
The process of making injection molds is a complex and precise engineering task that involves several steps, from initial design to final production. High-quality molds are essential for producing consistent, high-quality plastic parts. Advances in CAD software, CNC machining, and EDM technology have significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of mold making. Proper material selection, heat treatment, surface finishing, and rigorous testing ensure that the molds can withstand the demands of mass production and produce parts that meet stringent quality standards.
Related Conten: Plastic Injection Molding