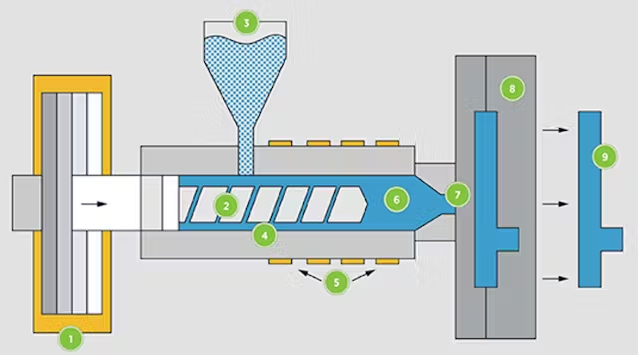
Plastic injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for producing plastic parts. It involves injecting molten plastic material into a mold, where it cools and solidifies into the final product shape. Here’s a detailed look at how plastic injection molding works:
Key Components of an Injection Molding Machine
- Injection Unit:
- Hopper: Holds the plastic pellets or granules before they enter the machine.
- Barrel: Heats and melts the plastic material.
- Screw: Moves the molten plastic forward and builds up pressure to inject it into the mold.
- Nozzle: Directs the molten plastic into the mold cavity.
- Clamping Unit:
- Mold: Consists of two halves, the core and the cavity, which shape the final part.
- Clamping Mechanism: Holds the mold halves together with sufficient force to withstand the injection pressure.
- Control System:
- Manages the various machine parameters such as temperature, injection pressure, and cycle time.
The Injection Molding Process
- Material Preparation:
- Plastic Pellets: The raw material, usually in pellet form, is fed into the hopper. Common materials include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), and ABS.
- Melting and Mixing:
- Heating: The barrel contains heaters that melt the plastic pellets as they are moved forward by the rotating screw.
- Mixing: The screw also helps mix the molten plastic to ensure uniform temperature and consistency.
- Injection:
- Filling: Once the plastic is melted and homogenized, the screw pushes the molten plastic through the nozzle into the mold cavity.
- Pressure: High pressure ensures the mold cavity is completely filled, and any intricate details are captured.
- Cooling:
- Solidification: The plastic cools and solidifies in the mold, taking the shape of the cavity.
- Cooling Time: This is a crucial phase, as proper cooling affects the final part’s quality and dimensional stability.
- Mold Opening:
- Ejection: After the part has cooled sufficiently, the clamping unit opens the mold, and ejector pins push the part out of the cavity.
- Cycle Repetition:
- The mold closes again, and the process repeats for the next cycle. This cycle time can range from a few seconds to several minutes, depending on the part size and complexity.

Choose us for your custom injection molding needs and experience excellence in every detail. Our China-based factory provides innovative solutions, competitive pricing, and fast turnaround times. Get your custom quote now!
Advantages of Plastic Injection Molding
- High Efficiency: Capable of producing large volumes of parts quickly and consistently.
- Complex Designs: Can create intricate shapes and detailed features that would be difficult or impossible with other manufacturing methods.
- Material Variety: Compatible with a wide range of thermoplastics, allowing for versatility in product properties.
- Low Waste: Excess plastic can often be recycled, reducing material waste.
Applications
Plastic injection molding is used across various industries due to its versatility and efficiency. Common applications include:
- Automotive: Dashboard components, bumpers, and interior trims.
- Consumer Goods: Toys, household items, and electronics housings.
- Medical Devices: Syringes, medical equipment housings, and disposable instruments.
- Packaging: Caps, containers, and lids.
Conclusion
Plastic injection molding is a powerful manufacturing process that combines efficiency, versatility, and precision to produce a wide range of plastic parts. By understanding the key components and steps involved in the process, manufacturers can optimize their production and achieve high-quality results suitable for various applications.
Related Conten: https://www.m-dtg.com/service/plastic-assembly-decoration/