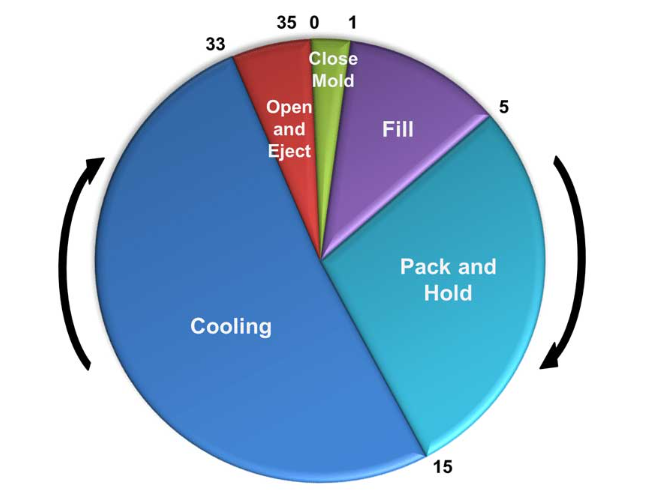
Cooling time in injection molding is the period during which the molten plastic solidifies and cools down inside the mold before the part is ejected. It is a critical phase in the injection molding cycle because it significantly affects the quality of the molded part and the overall cycle time, which in turn impacts production efficiency and costs.
Key Aspects of Cooling Time
- Role in the Injection Molding Cycle
- Solidification: During the cooling time, the molten plastic transitions from a liquid state to a solid state, taking on the shape of the mold cavity.
- Shrinkage and Warpage: Proper cooling time ensures that shrinkage and warpage are controlled, leading to parts that meet dimensional tolerances and have good surface finishes.
- Factors Affecting Cooling Time
- Material Properties: Different plastics have different thermal conductivities and heat capacities, affecting how quickly they can cool and solidify.
- Wall Thickness: Thicker parts take longer to cool than thinner parts. The cooling time is proportional to the square of the wall thickness.
- Mold Temperature: Lower mold temperatures can reduce cooling time, but they must be balanced with the need for proper part formation and surface quality.
- Mold Design: Efficient mold design, including cooling channels, helps to remove heat quickly and uniformly from the molded part.
- Cooling Channel Design: The placement, size, and efficiency of cooling channels within the mold play a crucial role in determining the cooling rate.
- Importance of Optimizing Cooling Time
- Part Quality: Proper cooling is essential to avoid defects such as sink marks, internal stresses, and warping. It ensures that the part retains its shape and dimensions.
- Cycle Time: Cooling time often constitutes a significant portion of the total cycle time. Reducing cooling time without compromising part quality can significantly improve production efficiency.
- Energy Consumption: Efficient cooling reduces the energy required to run the injection molding machine and auxiliary equipment, lowering overall production costs.
[elementor-template id=”4330″]
Calculating Cooling Time
Cooling time can be estimated using various empirical formulas, with one common approach being based on the thermal properties of the material and the part geometry. A widely used formula is:
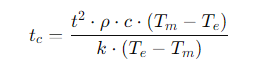
Where:

Reducing Cooling Time
- Optimizing Cooling Channels:
- Design cooling channels to be as close to the mold cavity as possible while maintaining uniform cooling. Conformal cooling channels, which follow the contour of the part, can be particularly effective.
- Using High Thermal Conductivity Materials:
- Utilize materials with higher thermal conductivity for the mold inserts to speed up heat transfer away from the part.
- Advanced Cooling Techniques:
- Implement advanced cooling methods such as beryllium copper inserts, conformal cooling, or even using coolant fluids with higher heat transfer capabilities.
- Cycle Time Optimization:
- Continuously monitor and adjust process parameters to ensure optimal cooling times. Using simulation software can help predict and optimize cooling time before actual production.
[elementor-template id=”4331″]
Conclusion
Cooling time is a crucial component of the injection molding process that directly affects the quality and efficiency of production. By understanding and optimizing the factors that influence cooling time, manufacturers can produce high-quality parts more efficiently, reducing costs and improving productivity
Related Conten: https://www.m-dtg.com/landing-page/custom-molders-corp/
 DTG Mould Trade Process |
|
| Quote: | According to sample, drawing and specific requirement. |
|---|---|
| Discussion | Mold material, cavity number, price, runner, payment, etc. |
| S/C Signature | Approval for all the items. |
| Advance | Pay 50% by T/T |
| Product Design Checking | We check the product design. If some position is not perfect, or can not be done on the mould, we will send customer the report. |
| Mold Processing | Send report to customer once each week |
| Mold Testing | Send trial samples and try-out report to customer for confirmation |
| Mold Modification | According to customer’s feedback. |
| Balance Settlement | 50% by T/T after the customer approved the trial sample and mould quality. |
| Delivery | Delivery by sea or air. The forwarder can be designated by your side. |
 |
|

